Kavach and AI-Driven Safety Transformation in Indian Railways
1. Kavach is India’s indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection system providing collision prevention, overspeed control, and Signal Passing at Danger protection through continuous monitoring and automatic braking interventions nationwide.
2. Kavach has been implemented on more than 2,200 route kilometres, reflecting large scale deployment of indigenous ATP technology across critical corridors of the Indian Railways network nationwide infrastructure.
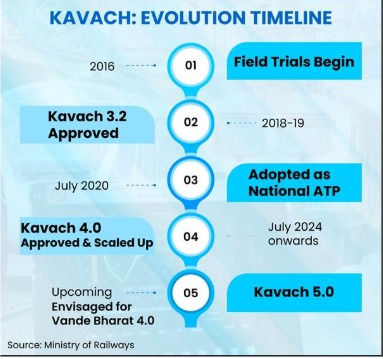
3. Kavach Version 4.0 operates over 1,306.3 route kilometres across five railway zones, strengthening safety on high speed, high density corridors such as Delhi–Mumbai and Delhi–Howrah trunk routes, nationally.
4. Vande Bharat 4.0 trains are envisaged to incorporate Kavach 5.0, enabling reduced headway, higher suburban frequency, and advanced automatic safety enforcement for future operations across major rail sections.
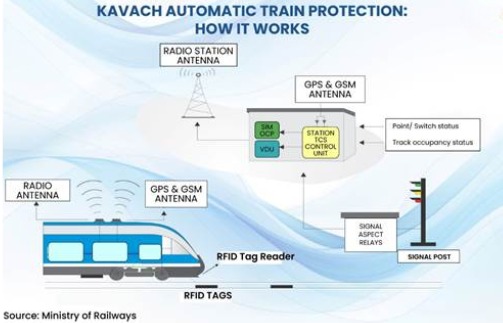
5. Kavach provides in cab signalling to loco pilots, displaying movement authority, target speed, target distance, and signal aspects for safer operations beyond 120 kilometres per hour thresholds nationally.

6. Developed by RDSO, Kavach mitigates risks arising from human error, equipment failure, and operational limitations through real time situational awareness and automated intervention mechanisms across diverse railway conditions.
7. Kavach uses secure UHF radio communication and RFID tags to determine precise train location while wayside units integrate interlocking, occupancy, and route data continuously for safe authority computation.
8. The system automatically applies brakes if a train overspeeds, approaches a danger signal, or enters a conflicting route, preventing collisions and Signal Passing at Danger incidents nationwide deployment.
9. Kavach supports Stop on Sight commands, ensuring automatic stoppage when two trains move toward each other in block sections, preventing head on and rear end collisions during operations.
10. Kavach is certified to Safety Integrity Level four, representing the highest global railway signalling safety standard and ensuring fail safe train protection under all conditions across Indian Railways.
11. Consequential train accidents declined significantly from 135 in 2014–15 to 31 in 2024–25 and further to 11 during 2025–26, reflecting technology driven safety gains across national rail corridors.
12. Indian Railways increased safety expenditure steadily from ₹39,200 crore in 2013–14 to ₹1,17,693 crore in 2025–26, underscoring long term institutional commitment towards infrastructure modernisation, accident prevention, resilience, nationally.
13. Kavach was adopted as the national Automatic Train Protection system in July 2020, enabling standardized deployment of interoperable safety architecture across Indian Railways networks, corridors, operations, zones, nationwide.
14. Kavach Version 4.0 commissioning prioritises High Density and Highly Used Network routes, including corridors cleared for 160 kilometres per hour operations with ABS and CTC signalling, control, systems.
15. AI enabled intrusion detection, predictive maintenance, video analytics, and digital communication systems complement Kavach, creating an integrated, preventive, and technology driven railway safety ecosystem across passengers, assets, operations.
Must Know Terms :
1.Kavach
Kavach is India’s indigenously developed Automatic Train Protection system adopted as the national ATP by Indian Railways in 2020. It prevents train accidents by monitoring speed, signal compliance, and train movement in real time. Kavach automatically applies brakes during unsafe conditions, significantly reducing human error–induced accidents and enhancing operational safety across high-density rail corridors.
2.Automatic Train Protection (ATP)
Automatic Train Protection refers to systems that continuously supervise train movement, speed, and signal adherence, intervening automatically when unsafe conditions arise. ATP systems prevent Signal Passing at Danger, overspeeding, and collisions. With increasing traffic density and higher speeds, ATP has become essential to maintain safety, reliability, and capacity on modern railway networks like Indian Railways.
3.Safety Integrity Level–4 (SIL-4)
SIL-4 is the highest internationally recognised safety certification for railway signalling systems. Kavach’s SIL-4 certification indicates extremely high reliability, fail-safe design, and minimal probability of dangerous failure. This level ensures that even under component failure or adverse conditions, the system defaults to safe states, making it suitable for high-speed and high-density railway operations.
4.Signal Passing at Danger (SPAD)
Signal Passing at Danger occurs when a train crosses a stop signal without authorisation, often leading to collisions. SPAD has historically been a major cause of serious rail accidents. Kavach directly addresses this risk by automatically stopping trains before danger signals, reducing dependence on human vigilance and significantly improving safety, especially under fog, curves, or poor visibility conditions.
5.Stop-on-Sight (SoS)
Stop-on-Sight is an automated safety command within Kavach that activates when two trains are detected moving toward each other in block sections. The system immediately applies brakes on both trains, preventing head-on or rear-end collisions. SoS is critical in non-interlocked or high-risk sections, providing a last-line defence against catastrophic accidents in real time.
6.AI-enabled Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
The AI-enabled Intrusion Detection System uses Distributed Acoustic Sensing technology to detect animal movement, particularly elephants, on railway tracks. It generates real-time alerts for loco pilots and control rooms, enabling preventive action. Deployed in vulnerable corridors, IDS reduces wildlife casualties, train derailment risks, and service disruptions, integrating ecological protection with railway safety objectives.
| Advantages of Kavach |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Key Takeaways
|
MCQ
1. Kavach is best described as which of the following systems?
A) Passenger Information System
B) Automatic Train Protection system
C) Train Scheduling Software
D) Track Maintenance Mechanism
2. Kavach has been developed indigenously by Indian Railways through which organisation?
A) DMRC
B) IIT Kanpur
C) RDSO
D) ISRO
3. Kavach primarily helps in preventing which of the following railway incidents?
A) Track corrosion
B) Signal Passing at Danger
C) Coach overcrowding
D) Power supply failure
4. Kavach provides in-cab display information to the loco pilot related to:
A) Passenger occupancy
B) Ticketing status
C) Movement authority and speed
D) Weather forecasting
5. Kavach Version 4.0 is currently operational across how many railway zones?
A) Three
B) Four
C) Five
D) Seven
6. Approximately how many route kilometres are covered under Kavach Version 4.0?
A) 750
B) 1,050
C) 1,306
D) 2,200
7. Kavach has now been implemented on more than how many route kilometres overall?
A) 1,000
B) 1,500
C) 2,200
D) 3,500
8. Kavach is certified to which Safety Integrity Level?
A) SIL-1
B) SIL-2
C) SIL-3
D) SIL-4
9. Kavach uses which combination for real-time communication and train location detection?
A) Satellite and GPS
B) Optical fibre and sensors
C) UHF radio and RFID tags
D) Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
10. Which Kavach version is envisaged to be incorporated in Vande Bharat 4.0 trains?
A) Kavach 3.2
B) Kavach 4.0
C) Kavach 5.0
D) Kavach Advanced Plus
11. The Stop-on-Sight (SoS) feature of Kavach is used primarily to prevent:
A) Fire accidents
B) Level crossing mishaps
C) Train collisions in block sections
D) Platform overruns
12. Indian Railways adopted Kavach as the National Automatic Train Protection system in which year?
A) 2016
B) 2018
C) 2020
D) 2022
13. Consequential train accidents declined from 135 in 2014–15 to how many in 2024–25?
A) 11
B) 21
C) 31
D) 41
14. Which of the following routes was among the first to be commissioned with Kavach 4.0?
A) Mumbai–Chennai
B) Palwal–Mathura–Nagda
C) Guwahati–New Jalpaiguri
D) Chennai–Bengaluru
15. AI-enabled Intrusion Detection System under Indian Railways is mainly used to detect:
A) Track fractures
B) Equipment theft
C) Wild animal movement
D) Signal malfunction



0 comment